Delving into Small Business Health Insurance: What You Need to Know, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, with a casual formal language style that is both engaging and thought-provoking from the very first sentence.
Explaining the intricacies of small business health insurance, this paragraph sets the stage for a comprehensive discussion on the topic.
Overview of Small Business Health Insurance
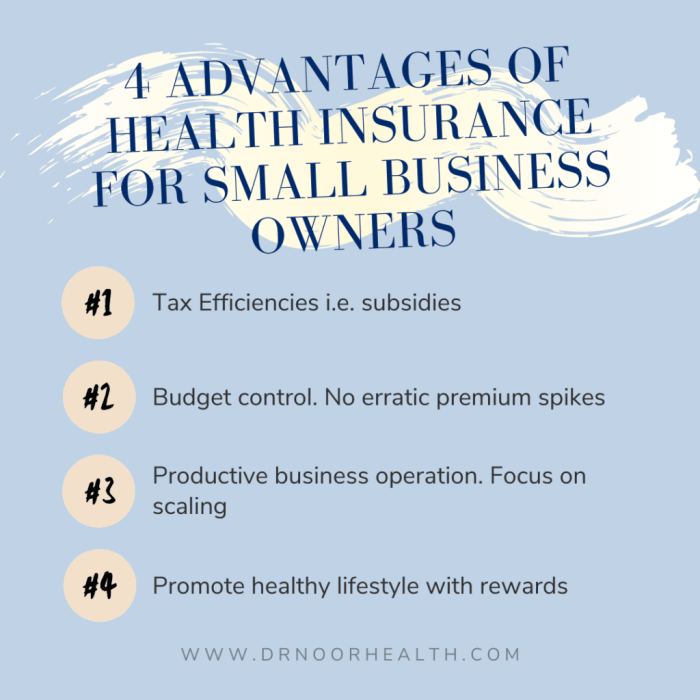
Small business health insurance is a crucial benefit that employers can offer to their employees. It provides coverage for medical expenses, ensuring that employees have access to necessary healthcare services.
Common Health Insurance Plans for Small Businesses
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): This plan requires employees to choose a primary care physician and obtain referrals to see specialists.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): Employees have the flexibility to see any healthcare provider, but will pay less out-of-pocket if they stay within the network.
- High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) with Health Savings Account (HSA): This plan has a high deductible which is paired with a tax-advantaged savings account for medical expenses.
Benefits of Offering Health Insurance to Employees
- Attracts and Retains Talent: Providing health insurance can make a small business more competitive in the job market, attracting top talent and reducing turnover.
- Improves Employee Health and Productivity: When employees have access to healthcare, they are more likely to seek preventive care, leading to better health outcomes and increased productivity.
- Tax Advantages: Small businesses may be eligible for tax credits when offering health insurance to employees, reducing the overall cost of coverage.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Health Insurance Plan
When selecting a health insurance plan for your small business, there are several key factors to keep in mind to ensure you make the best choice for your employees and your budget.
Group Health Insurance vs. Individual Health Insurance
Group health insurance is typically offered to a group of employees through their employer, providing coverage for all members of the group. Individual health insurance is purchased by individuals to cover themselves and their families. Group plans often have lower premiums compared to individual plans due to the risk being spread across a larger group of individuals.
Premiums, Deductibles, and Co-pays
Premiums are the amount you pay upfront for your health insurance coverage, usually on a monthly basis. Deductibles are the amount you must pay out of pocket before your insurance kicks in, while co-pays are fixed amounts you pay for specific services.
When choosing a health insurance plan, it’s important to consider how premiums, deductibles, and co-pays will impact your employees’ out-of-pocket costs and overall affordability of the plan.
Legal Requirements and Regulations
Small businesses offering health insurance must adhere to certain legal requirements and regulations to ensure compliance with the law. One key piece of legislation that impacts small business health insurance is the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which was enacted in 2010.
Affordable Care Act Impact
The ACA requires businesses with 50 or more full-time employees to offer affordable health insurance coverage that meets certain minimum requirements. This includes providing essential health benefits, such as preventive care, maternity care, and mental health services. Small businesses with fewer than 50 employees are not required to provide health insurance, but they may be eligible for tax credits if they choose to do so.
- Small Business Health Care Tax Credit: The ACA offers a tax credit to small businesses with fewer than 25 full-time equivalent employees who provide health insurance coverage to their employees. To qualify for the tax credit, the employer must contribute at least 50% of the employee’s premium costs and meet certain other requirements.
- Employer Shared Responsibility Provision: Under the ACA, businesses with 50 or more full-time employees may be subject to penalties if they do not offer affordable health insurance that meets minimum standards. This provision is aimed at encouraging large employers to provide health insurance coverage to their workers.
Cost Management Strategies
Managing health insurance expenses is crucial for small businesses to ensure financial stability. By implementing cost-effective strategies, businesses can provide quality healthcare coverage to employees without breaking the bank.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
- HSAs allow employees to contribute pre-tax dollars to an account specifically designated for medical expenses.
- Employers can also contribute to employees’ HSAs, providing an additional benefit.
- Funds in HSAs roll over from year to year, offering long-term savings potential for both employees and employers.
- Employees can use HSA funds to pay for qualified medical expenses, reducing out-of-pocket costs.
Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs)
- HRAs are funded solely by the employer and provide a way to reimburse employees for medical expenses.
- Employers have control over the amount contributed to HRAs, allowing for flexibility in managing costs.
- HRAs can be tailored to cover specific medical expenses or services, providing targeted cost savings.
- Unused HRA funds can potentially be rolled over to the next year, offering additional cost management benefits.
Negotiating with Insurance Providers
- Research different insurance providers to compare rates and coverage options.
- Consider bundling insurance policies or negotiating for discounts based on the number of employees covered.
- Highlight the overall health of your employee population to potentially lower premium costs.
- Discuss cost-sharing options with insurance providers to find a plan that fits your budget and coverage needs.
Employee Communication and Education
When it comes to small business health insurance, educating employees about their coverage is crucial. Understanding their benefits can lead to better utilization of healthcare services and overall satisfaction with the plan.
Importance of Educating Employees
- Helps employees make informed decisions about their healthcare needs.
- Increases appreciation for the benefits provided by the employer.
- Reduces confusion and misunderstandings regarding coverage and costs.
Best Practices for Communication
- Provide clear and concise communication about any changes in health insurance plans.
- Use multiple channels such as emails, meetings, and handouts to reach all employees.
- Offer one-on-one sessions for employees to ask questions and clarify doubts.
Tips for Understanding Coverage and Benefits
- Encourage employees to read through their plan documents and ask HR for clarification if needed.
- Highlight key benefits like preventive care coverage and wellness programs available.
- Explain how deductibles, co-pays, and co-insurance work to manage out-of-pocket costs.
Comparison of Different Health Insurance Providers
When it comes to choosing a health insurance provider for your small business, it’s important to compare and contrast the options available to find the best fit for your company’s needs. Each insurance company has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s crucial to evaluate them based on certain criteria.
Popular Health Insurance Providers
- Blue Cross Blue Shield: Known for its wide network of healthcare providers, but may have higher premiums.
- Aetna: Offers comprehensive coverage options, but customer service can sometimes be lacking.
- Cigna: Provides customizable plans and wellness programs, but may have limited network options.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Providers
- Blue Cross Blue Shield: Extensive network coverage, but potentially higher costs.
- Aetna: Comprehensive plans, but possible issues with customer support.
- Cigna: Customizable options, but limited provider networks.
Criteria for Evaluating Health Insurance Providers
- Network Coverage: Check if your preferred healthcare providers are in-network.
- Cost: Compare premiums, deductibles, and copayments for affordability.
- Plan Customization: Look for plans that can be tailored to your employees’ needs.
- Customer Service: Research reviews and ratings to assess the quality of service.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, this discussion on Small Business Health Insurance: What You Need to Know sheds light on the crucial aspects that every small business owner should be aware of. It is essential to navigate the realm of health insurance with knowledge and understanding to make informed decisions for the well-being of your employees and business.
Popular Questions
What are the common health insurance plans available for small businesses?
Common health insurance plans for small businesses include Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), and High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs).
How does the Affordable Care Act impact small business health insurance?
The Affordable Care Act requires small businesses with 50 or more full-time employees to provide health insurance or face penalties. It also offers the Small Business Health Care Tax Credit to eligible small businesses to help cover the cost of providing insurance to employees.
What are Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs)?
HSAs are tax-advantaged savings accounts that individuals can use to pay for qualified medical expenses, while HRAs are employer-funded arrangements that reimburse employees for out-of-pocket medical expenses.